S.Antonious, S.Yuvarajan, R.Praveen,A. Arun Kumar, R.Santhiya, S.Kamal Barathi
Department of Respiratory Medicine, Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College, Pondicherry, India.
Background and AIMS
Mucormycosis is an opportunistic infection that is caused by Mucorales fungi of the Zygomycetes class. Pulmonary mucormycosis is an uncommon, life-threatening opportunistic fungal infection which affects immunocompromised patients such as diabetes, recipients of stem cell or organ transplant, and has worse outcomes in those with hematologic malignancy or neutropenia.
Methods
A 35 years old male patient with uncontrolled type II Diabetes mellitus presented to casualty with complaints of cough associated with thick dark brownish sputum for 1 month, fever, loss of appetiteand loss of weight since 15 days. His vitals were stable at the time of admission. Chest auscultation revealed diminished vesicular breath sounds heard in rightinfraclavicular and suprascapular area.
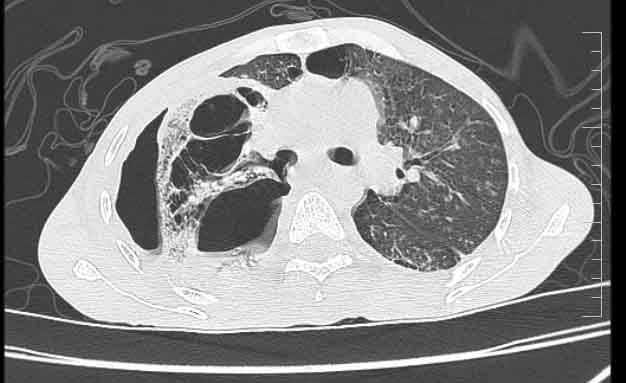
Complete blood count showed leukocytosis with neutrophilic predominance. He also had hyonatremia and hypokalemia. Chest x-ray showed large irregular thick walled cavity in right mid zone extending to the lower zone. CT thorax revealed central bronchopleural fistulainvolving right main bronchus with collapse and consolidation involving right middle and lower lobe.
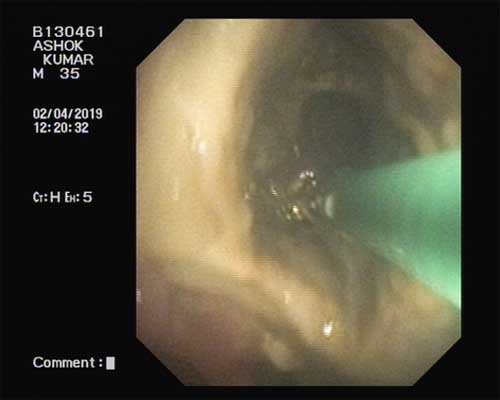
Patient underwentdiagnostic bronchoscope which showed distorted right secondary carina and there was a large communication in right main bronchus extending to pleural space with thick brownish collection.Right upper lobe bronchial mucosa was unhealthy, covered with a thick brownish slough.
Result
Bronchoalveolar lavage for KOH smear and showed broad aseptate hyphae with right angle branching. Transbronchial lung biopsy taken from right upper lobe bronchial mucosa was suggestive of predominant necrotic mass with scattered fibrous strands and fungal organisms with broad aseptate hyphae which was morphologically consistent with Mucormycosis. Patient was started on intravenous amphotericin deoxycholate and syrup Posaconazole. Cardiothoracic surgeon opinion was sought out in view of large Bronchopleural fistula and the patient underwent right pneumonectomy.
Conclusion
Weevidenced a positive clinical outcome in a poorly controlled diabetic state with early surgical resection and a combination of antifungals. It highlights the importance of the early diagnosis, treatment and timely surgical debridement for the therapy of mucormycosis.